Durhane Wong-Rieger, PhD, President, Anemia Institute for Research & Education.
Anemia affects tens of thousands of Canadians, including many older people. While some types of anemia are relatively easy to diagnose and treat, complications such as chronic disease or complex medication regimes can often interfere with diagnosis and management of this condition.
 The Anemia Institute for Research & Education (AIRE) is the first and only nonprofit organization in the world committed entirely to generating and sharing knowledge about anemia. AIRE supports patients in understanding anemia, its causes, effects and the available treatment options. The Institute partners with numerous patient and professional groups to facilitate patient education on anemia and blood safety and supply. Furthermore, through a yearly research grant competition, AIRE sponsors numerous anemia research studies. All in all, the Anemia Institute is working hard to ensure that anemia is treated seriously.
The Anemia Institute for Research & Education (AIRE) is the first and only nonprofit organization in the world committed entirely to generating and sharing knowledge about anemia. AIRE supports patients in understanding anemia, its causes, effects and the available treatment options. The Institute partners with numerous patient and professional groups to facilitate patient education on anemia and blood safety and supply. Furthermore, through a yearly research grant competition, AIRE sponsors numerous anemia research studies. All in all, the Anemia Institute is working hard to ensure that anemia is treated seriously.
For Physicians: Anemia Guidelines for Primary Care
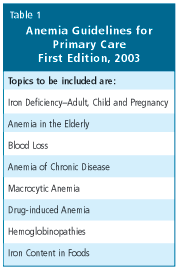
In a 2001 survey of family physicians across Canada, 90% of doctors indicated their interest in clinical practice guidelines on anemia for family practice. The Anemia Institute responded, initiating the development of Anemia Guidelines for Primary Care with MUMS Guidelines Clearinghouse (Medication Use Management Services), to be published in May 2003. The Anemia Guidelines is the fifth book in the Orange Book guideline series published by MUMS. This easy to use, peer-reviewed and fully-referenced book provides diagnostic and treatment guidelines for the full range of anemia conditions (see Table 1 for a selection of topics covered).
A limited number of complimentary copies of the Anemia Guidelines is available from AIRE. To order, please visit www.anemiainstitute.org and go to the Healthcare Professionals section.
For Your Patient: Anemia Educational Tools
The Anemia Institute's series of patient leaflets covers the most common types of anemia. Patient Educational Leaflets include:
- What is Anemia?
- What is Hemoglobin?
- Anemia & Nutrition
- Anemia & Iron Deficiency
- Anemia & Cancer
- Anemia & Kidney Disease
- Anemia & Surgery
- Anemia & Hepatitis C
- Anemia & HIV/AIDS
- Anemia & Children and Teens.
 Anemia Awareness Week is the Institute's yearly campaign to raise awareness of anemia among the general public. This takes place each year during the last week of March. In March 2003, the public were invited to visit numerous hemoglobin screening clinics and anemia display booths in pharmacies and hospitals across Canada. Similar events are planned for Anemia Awareness Week next year, March 22&endash;26, 2004.
Anemia Awareness Week is the Institute's yearly campaign to raise awareness of anemia among the general public. This takes place each year during the last week of March. In March 2003, the public were invited to visit numerous hemoglobin screening clinics and anemia display booths in pharmacies and hospitals across Canada. Similar events are planned for Anemia Awareness Week next year, March 22&endash;26, 2004.
Research & Development Fund
The Anemia Institute Research & Development Fund supports research initiatives through a yearly, peer-reviewed grant competition. Projects currently funded include:
- the role of anemia and red blood cell substitutes in traumatic brain injury;
- new strategies to treat post-transplant anemia;
- anemia among the inner city homeless.
More information on the AIRE research grant process, including funding priorities and application procedures, can be found on the Internet at www.anemia-institute.org.