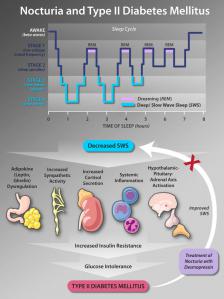
Diabetic Nephropathy is a diagnosis that refers to specific pathologic structural and functional changes seen in the kidneys of patients with DM.
This is a case of mr. JB. He’s a 64 year old man who has had type 2 diabetes for 10 years.
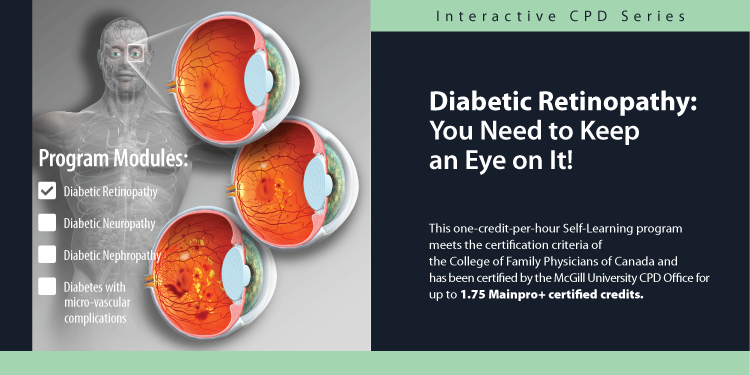
Mr. RH is a fifty year old male who was complaining of gradual vision loss in both eyes more so on his right than on his left.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasingly common, and previously unrecognized complications are emerging...
MD, FRCPC, FACP, AGSF
Research into the management of diabetes seems to be accelerating every year, and the large number of new treatment options makes it difficult for the average physician to keep up.
Advertisement
Recent therapeutic advances have seen the emergence of several oral agents for type 2 diabetes, providing an opportunity for better management of the disease.
Glycemic goals and the decision to intensify glycemic control among older adults with diabetes must be individualized based on comorbid conditions and the risks associated with treatment.
Over the past decade, eight classes of drugs have been used to treat diabetes; however, insulin remains the most effective and least costly treatment for older adults.
Self-management education and counselling regarding diet and physical activity can improve weight, blood glucose, and lipid levels, and blood pressure control among older adults with type 2 diabetes.