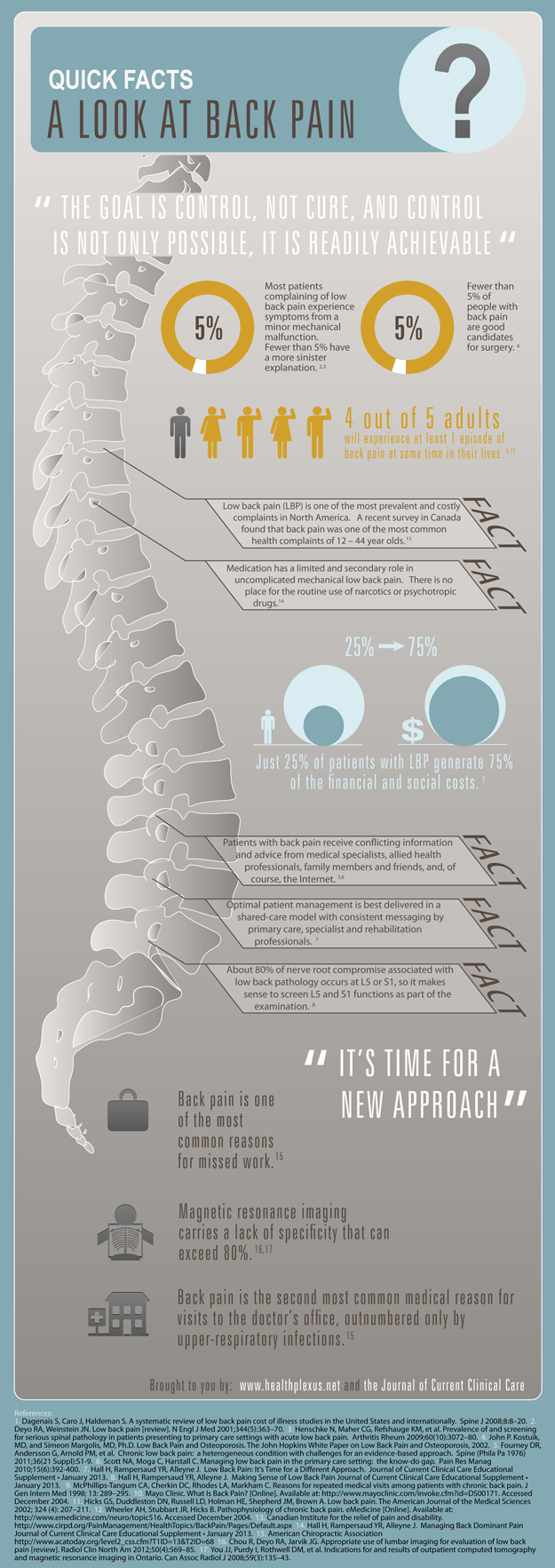
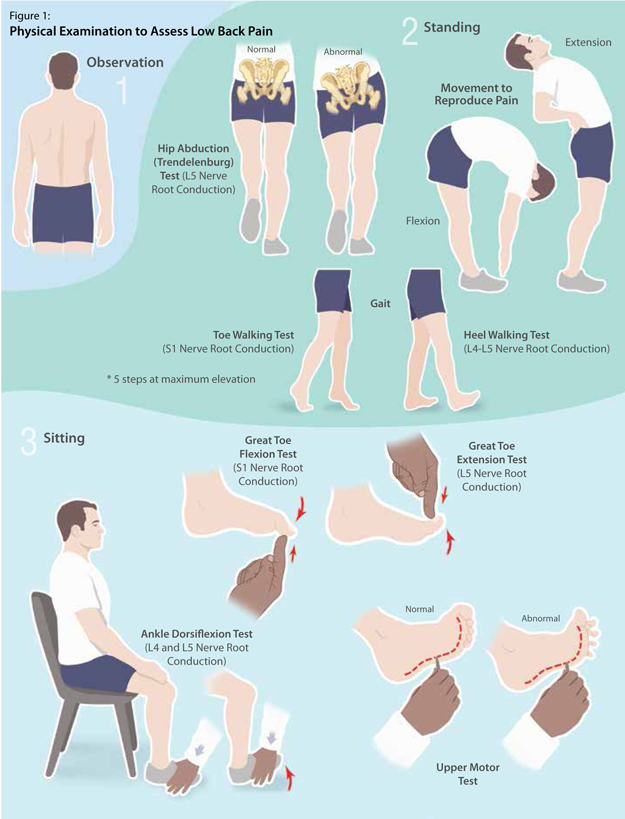
1Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto; Medical Director, Canadian Back Institute; Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society, Toronto, ON.
2Associate Professor, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Toronto, Medical Director, Sport CARE, Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, ON.
3Associate Professor Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Divisions of Orthopaedic and Neurosurgery, University Health Network Medical Director, Back and Neck Specialty Program, Altum Health, Immediate Past President Canadian Spine Society, Toronto, ON.