G. Tong, MD, PhD
Jody Corey-Bloom, MD, PhD
Department of Neurosciences,
University of California San Diego, CA, USA.
Introduction
Alzheimer disease (AD), the most common form of dementia in the elderly, is characterized clinically by multiple cognitive deficits, including memory loss, visuospatial impairment, disorientation and language dysfunction. These features are often accompanied by behavioural and mood changes. A definitive diagnosis of AD can only be made by biopsy or autopsy. The major neuropathological features of AD are neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.
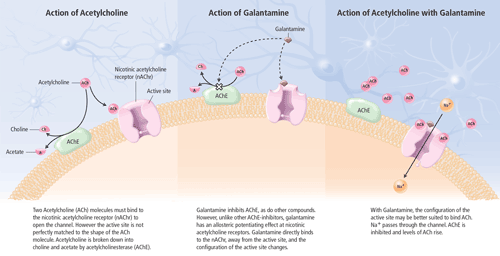
Cholinergic neurotransmission in the central nervous system (CNS) plays a key role in memory, attention, learning and other cognitive processes. Although other neurotransmitter deficiencies (e.g., noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin and glutamate) have been noted, the cognitive impairments seen in AD patients have been largely attributed to decreased cholinergic neurotransmission. AD, in part, is characterized by the loss of neurons in basal forebrain cholinergic cells, especially in the nucleus basalis of Meynert, which projects to the cerebral cortex and hippocampus.