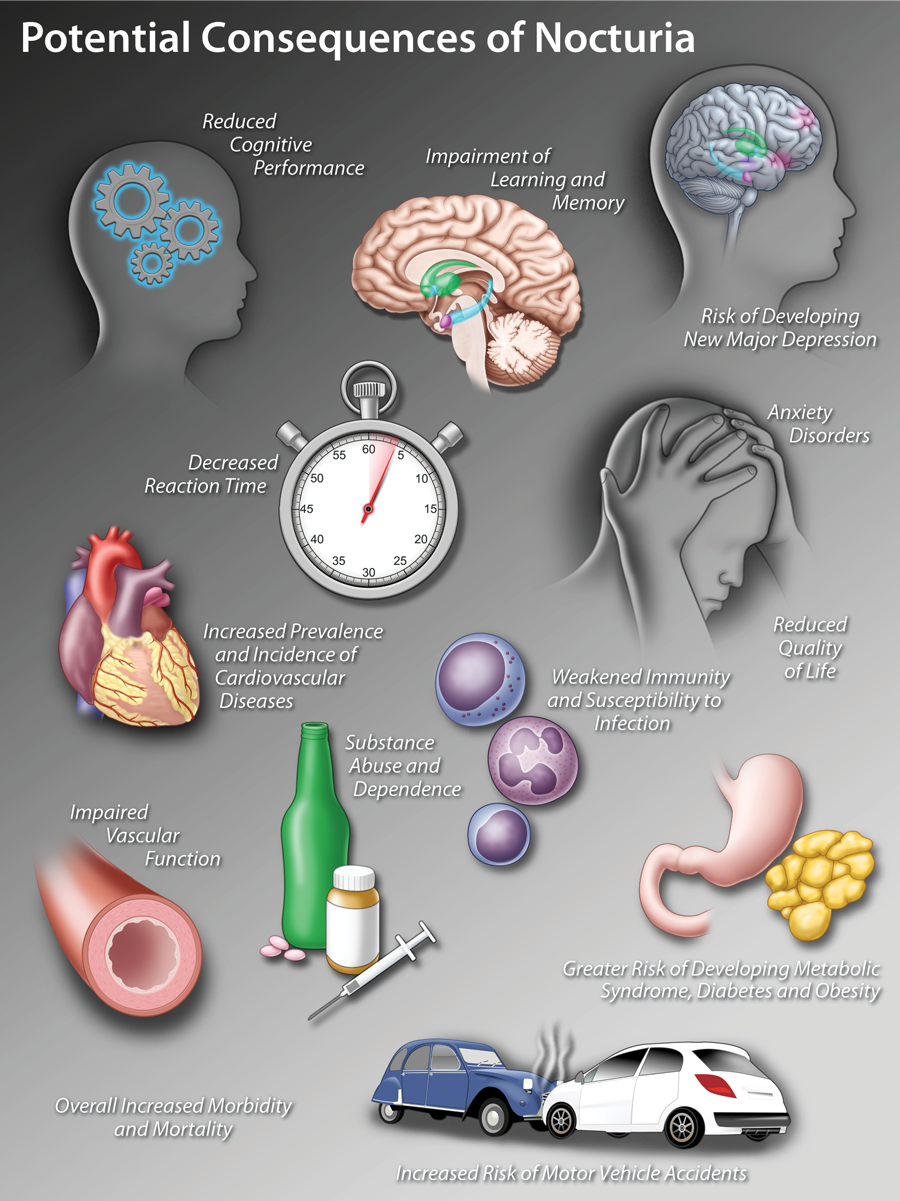
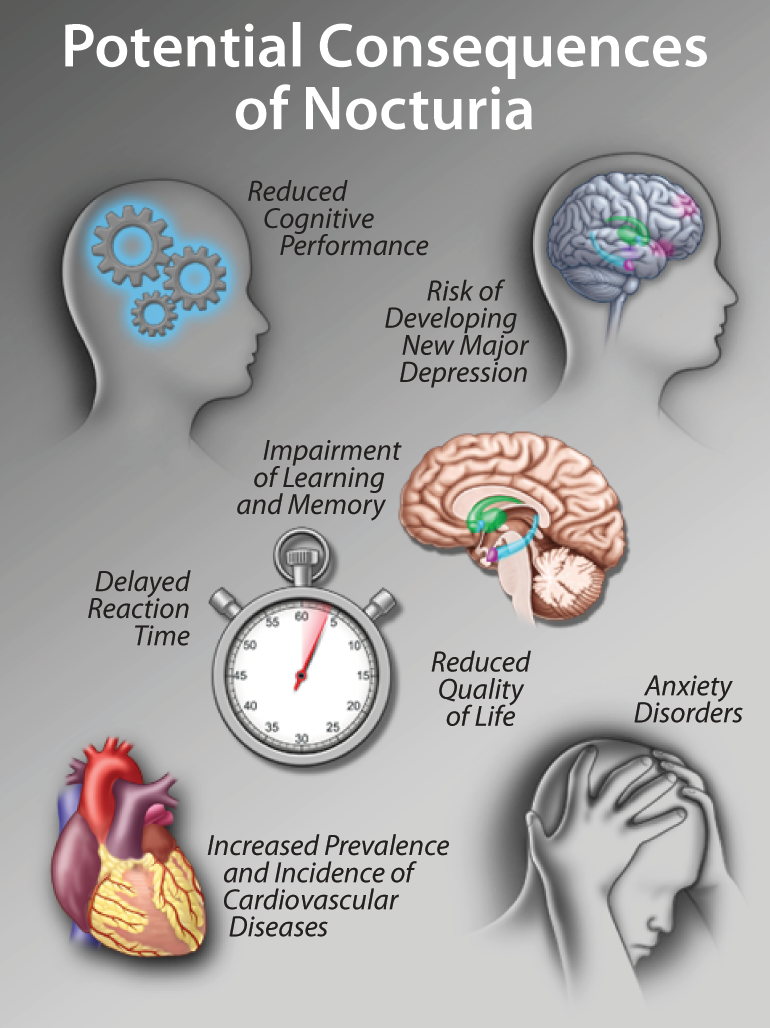
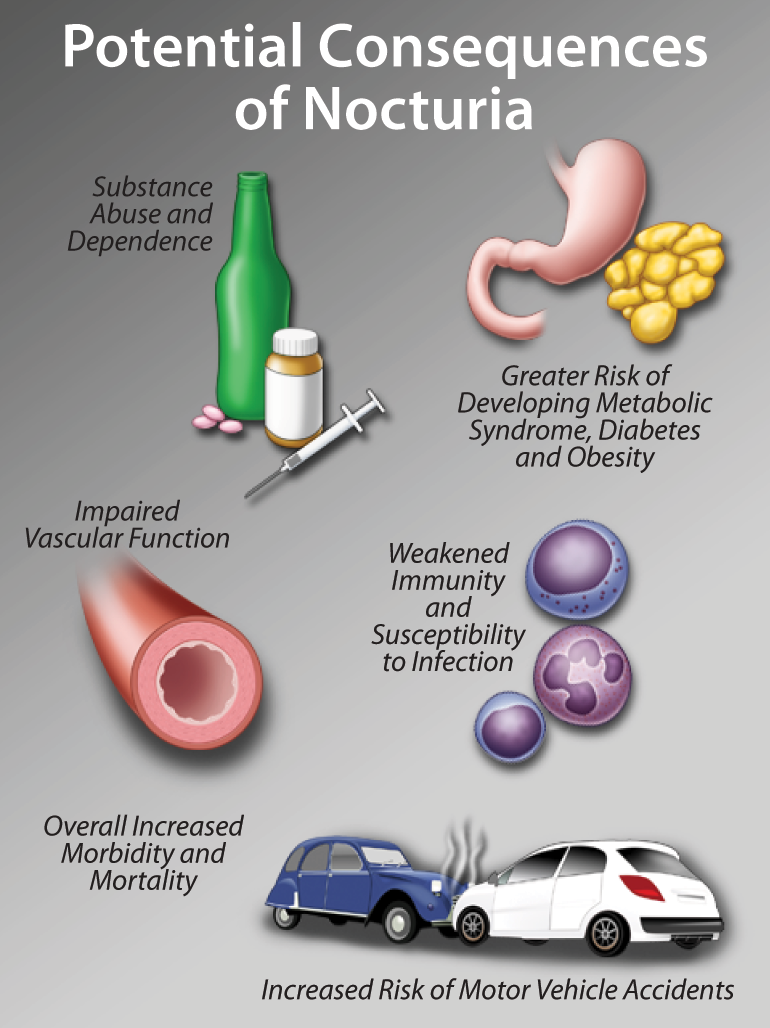
Nocturia and Sleep Disorders
Disclaimer:
This article was published as part of THE LATEST IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF NOCTURIA eCME resource.
The development of THE LATEST IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF NOCTURIA eCME resource was supported by an educational grant from Ferring Inc.