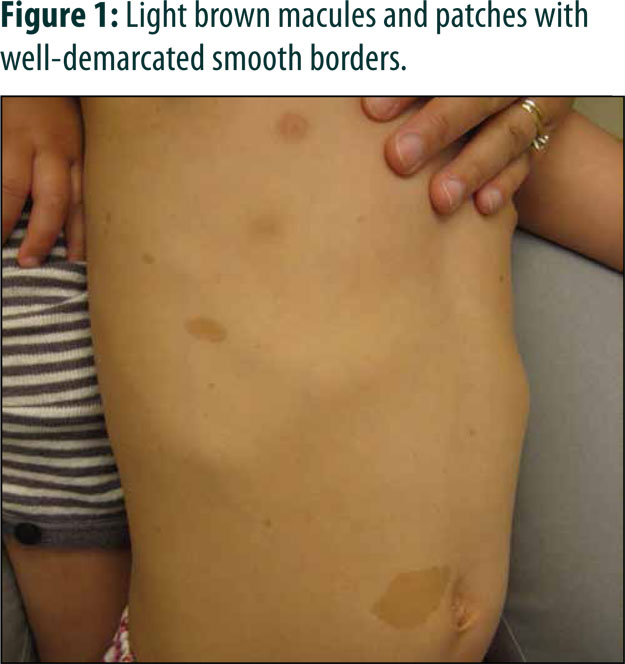
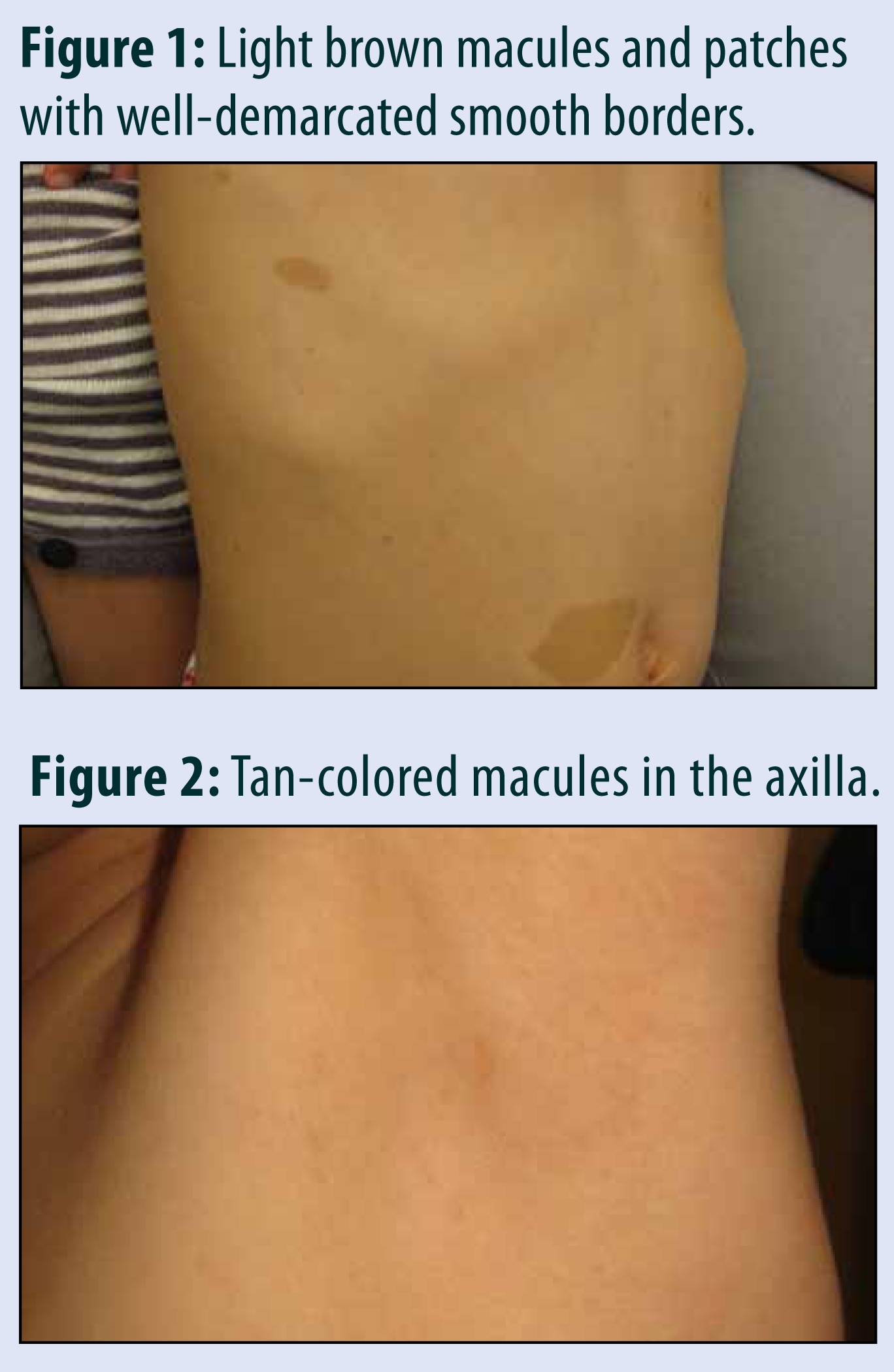
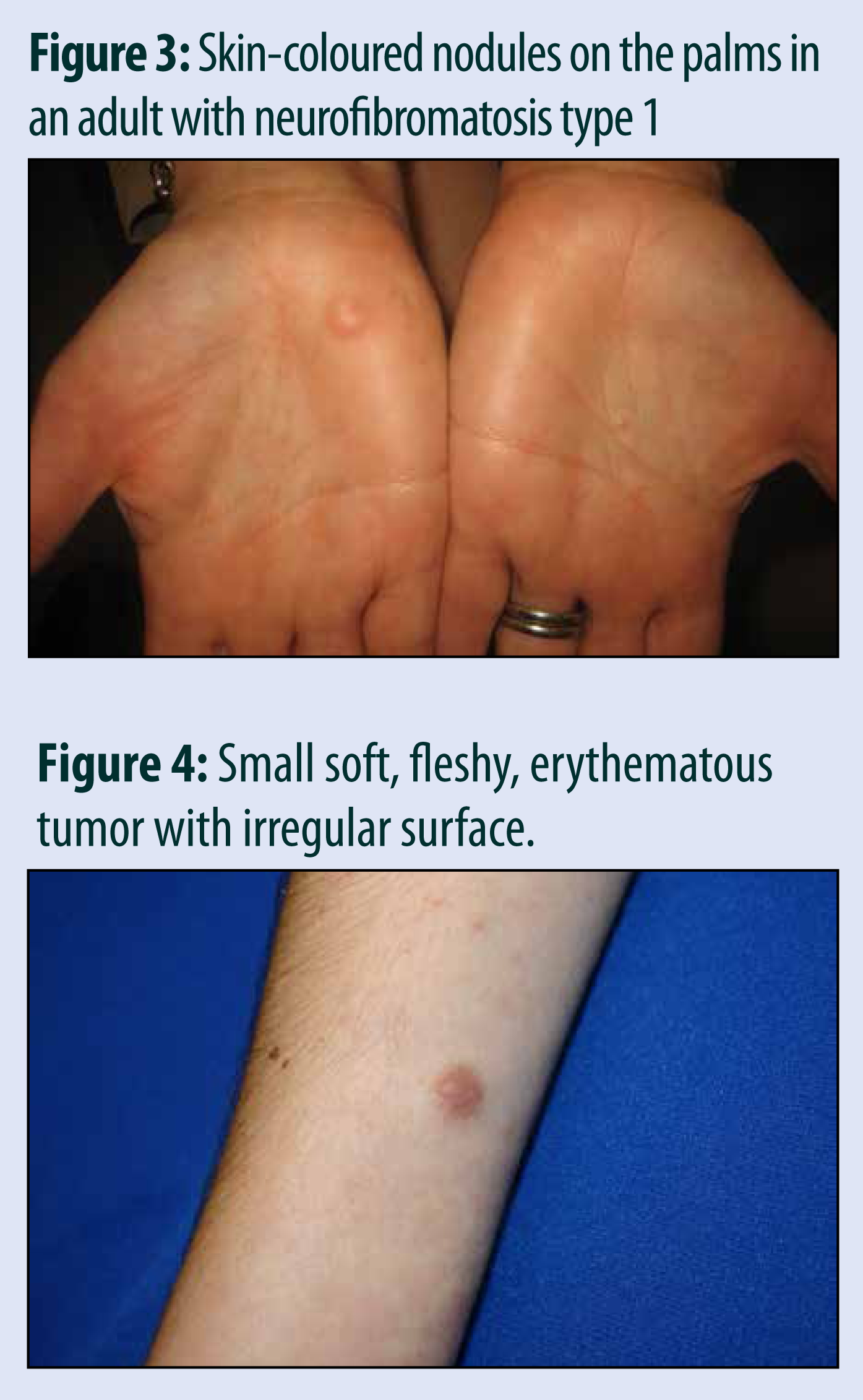
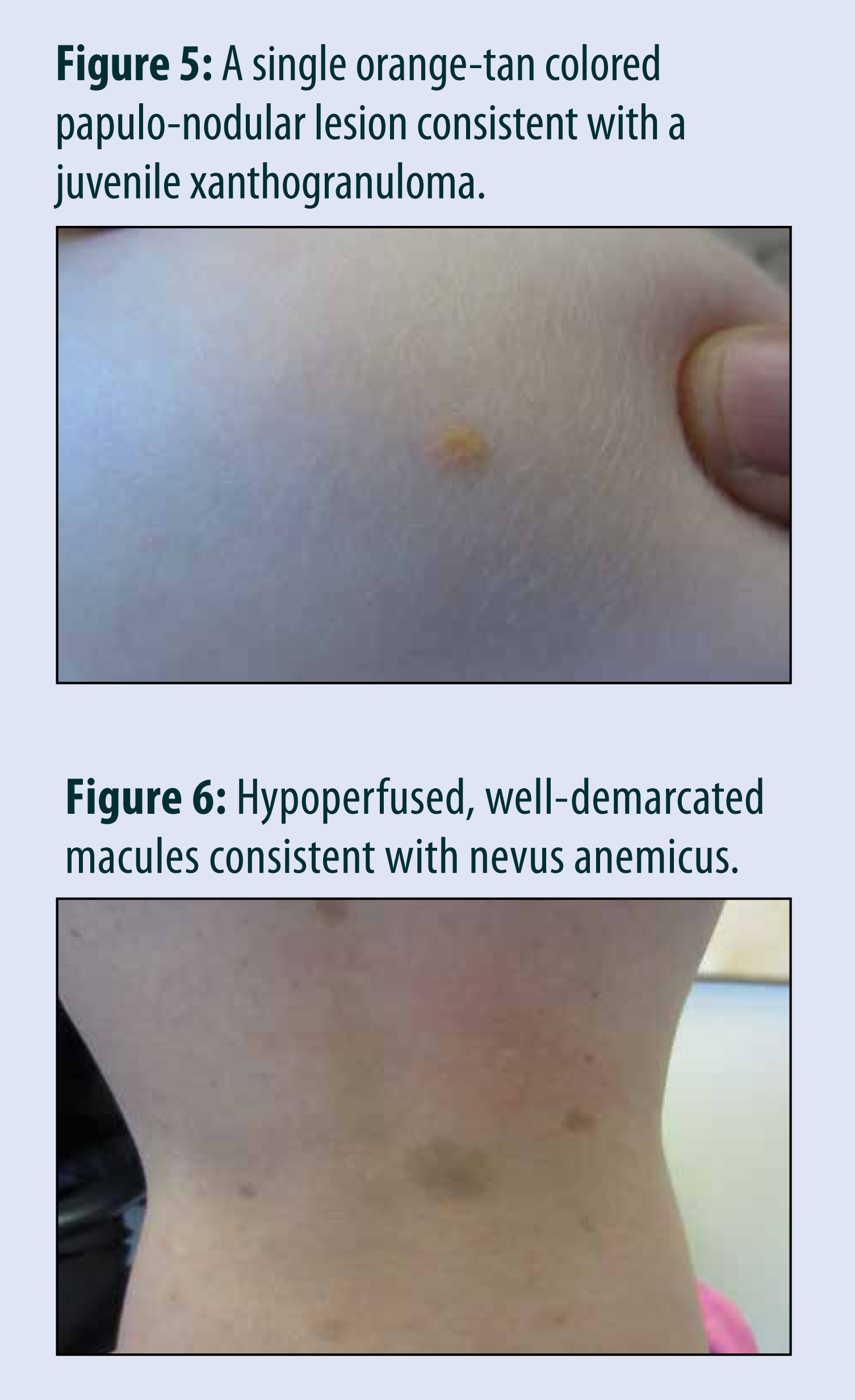
Advertisement
Advertisement
- inFocus
- Topics
- Addiction
- Arthritis
- Back Health
- Biology of Aging
- Cancer
- Cardio-Cerebrovascular
- Caregiving
- Dementia
- Dermatology
- Diabetes-Endocrine
- Drug Safety
- Eye Health
- Falls and Fitness
- Gastrointestinal Diseases
- Gender & Health
- Genetic Diseases
- Hematologic Disorders
- Incontinence
- Infectious Diseases
- Law and Ethics
- Liver Diseases
- Lung Diseases
- Medical Narratives
- Mental Health
- Men’s Health
- Musculoskeletal Disease
- Neurology-Movement
- Nutrition
- Oral Health
- Osteoporosis
- Otolaryngology
- Pain
- Palliative Care
- Perioperative Care
- Preventive Health
- Radiology
- Renal Diseases
- Sports Medicine
- Technology in Medicine
- Urogenital Disorders
- Women’s Health
- Other
- Posts
- Apps
- CPD/CME
- Journal
- Visual Aids
- Live Events