Introduction
The publication of the landmark Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study1 in the New England Journal of Medicine in January 2000 was greeted by a great deal of excitement in the medical community. In essence, the trial confirmed beyond a doubt the cardiac and renal protective benefit of ACE inhibition and extended the patient base in whom ACE inhibition has been proven effective. Our understanding of the cardioprotective nature of ACE inhibitors has been built over the years by the various mega-studies that have been conducted, dating back to the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS),2 published in 1987, which showed a 31% survival advantage for ACE inhibition in New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IV heart failure patients. Thirteen years and more than a dozen large trials later, the HOPE study has confirmed that patients need not be so sick--indeed, need only be considered at risk for cardiovascular events--for ACE inhibition to show similar benefits. Looking down the list, from CONSENSUS to HOPE and several landmark trials in between, one would be hard pressed to find a class of agents with a wealth of compelling evidence comparable to that accumulated for ACE inhibitors.
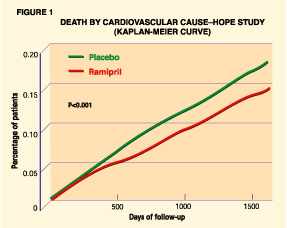 Main Results and Significance
Main Results and Significance
The HOPE study investigators found that 17.

 Main Results and Significance
Main Results and Significance