Thomas Tsirakis, BA
Social isolation is common amongst the elderly. Socially isolated individuals display significantly higher suicide rates, a greater number of physical and cognitive impairments, and a lower life expectancy rate when compared to those who are socially active. European studies have shown that even minor interventions to break social isolation, such as friendly visitors or routine volunteer phone calls, improve survival in the socially isolated elderly. The Baycrest Centre for Geriatric Care in Toronto, Ontario offers a wide range of innovative programs that specifically address problems with withdrawal and social isolation.
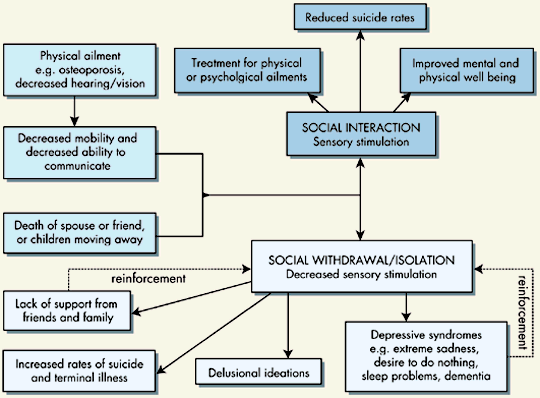
Studies show that the elderly population in general feels that their contributions to society are deemed to be insignificant by younger generations. Being able to contribute to the lives of others is important for building self-worth, and ultimately increases the value placed on life itself. For many older persons, various physical ailments (such as osteoporosis, and reduced level of vision and hearing) can cause a reduction in mobility and communication with others, ultimately causing social withdrawal. If the person's withdrawal becomes prolonged, it can become increasingly difficult to break free of this isolation.

