Neil Fam, BSc, MSc
Hepatitis refers to acute or chronic inflammation of the liver, with the majority of cases resulting from either viral infection or drugs. In Canada, hepatitis B and C infections are the most common cause of viral hepatitis, and may be associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. Globally, chronic viral hepatitis is the leading cause of chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma and is the most common indication for liver transplantation. This article provides an outline of the natural history of hepatitis B and C infections, and describes current approachs to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Unique aspects of hepatitis in the elderly are highlighted.
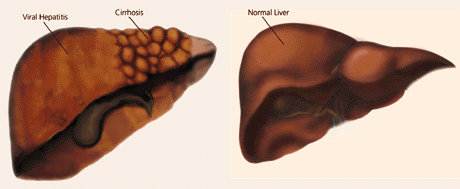
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a DNA virus that infects over 350 million people worldwide. Although HBV infection is extremely common in parts of Asia and Africa, Canada has a relatively low level of endemicity. In North America, HBV infection occurs mainly in sexually active young adults. Important risk factors for HBV include sexual activity, IV drug use, occupational exposure, travel or residence in an endemic area and previous blood transfusion. The route of transmission may be sexual, parenteral, or vertical, with an incubation period of 6 weeks to 6 months.

